The true bottleneck in modern supply chains isn’t inventory shortages- it’s the gap between physical movement and digital awareness. When tracking systems can’t keep pace with the real-time movement of goods, every delay becomes harder to diagnose, and every disruption is more expensive. Even the smartest supply chains stall when outdated systems can’t keep up with real-world movement.
Authored by: Stellium’s Automation Practice and I&ET team and verified by Karthik Krishnan and Hari Babu
Why RFID Is a Catalyst for Supply Chain Integration
Across industries, RFID plays a crucial role in enabling tightly integrated, collaborative supply chains. Its capabilities empower:
- End-to-End Visibility: Real-time, automated tracking across suppliers, plants, and logistics partners.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation replaces manual scanning, accelerating processes and reducing errors.
- Collaborative Planning: Accurate inventory data supports forecasting and production alignment.
- Traceability and Compliance: Product lifecycle tracking ensures regulatory readiness and quality control.
This transforms reactive operations into agile, predictive networks.
Benefits of RFID Adoption in Supply Chain
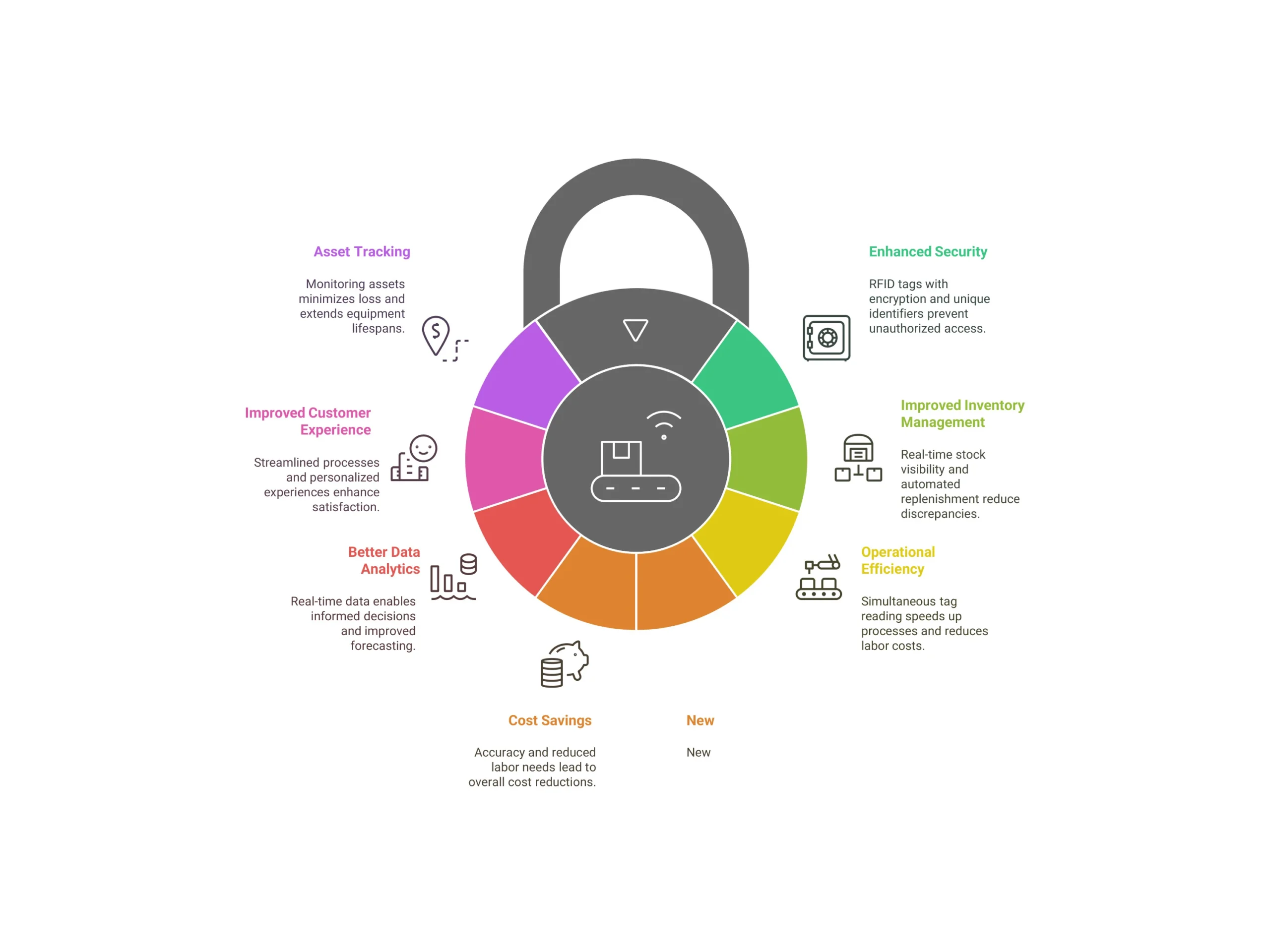
RFID Technologies: Choosing the Right Fit for Your Business
RFID isn’t one-size-fits-all. Depending on industry specific operational needs, businesses can choose from several types of tags, placement, and balancing the RFID performance. Industries often blend these for complete supply chain visibility.
Balancing RFID Performance
Effective RFID deployment hinges on achieving the right balance across four critical dimensions- accuracy, speed, range, and cost-effectiveness. These dimensions shape how RFID performs in real-world environments, particularly in high-pressure automotive operations.
Choosing the right RFID technology means finding the optimal balance across these four key performance dimensions:
Balancing RFID Performance Dimensions for Supply Chain
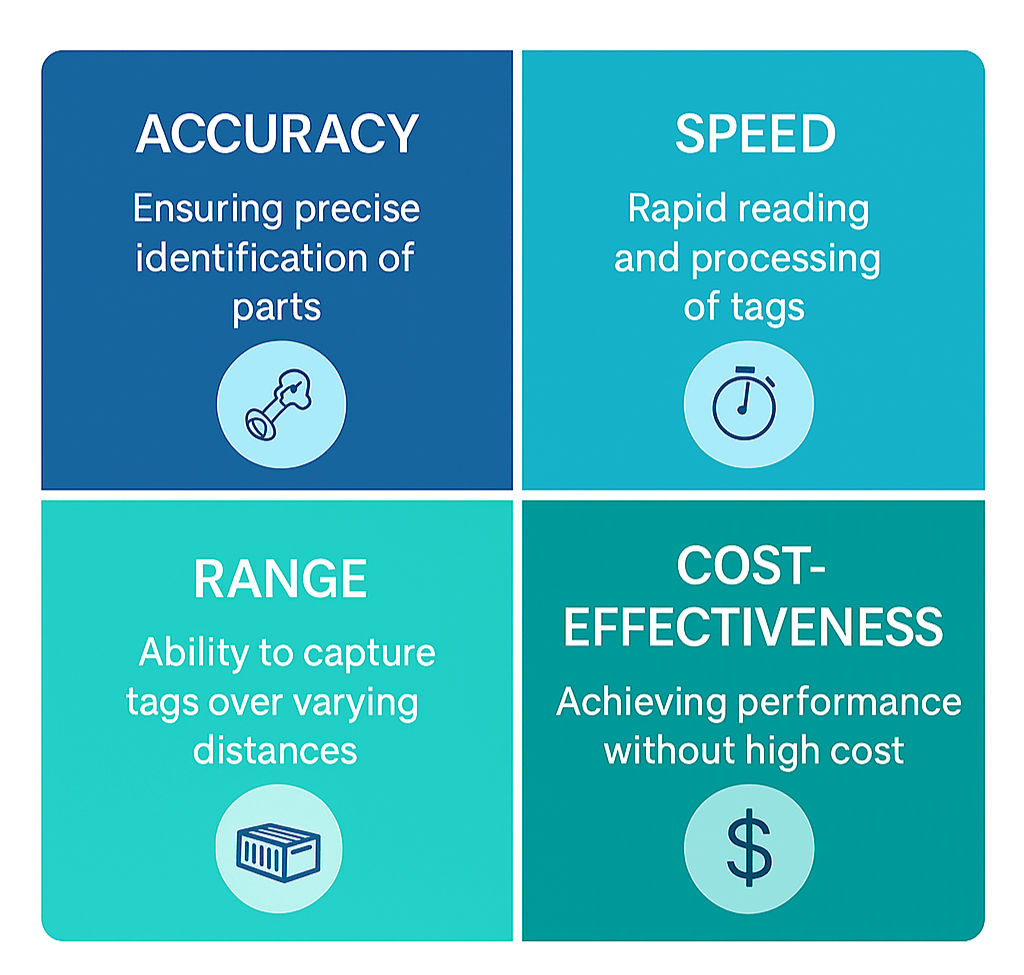
The effectiveness of RFID solutions depends on how well they balance key performance metrics with real-world operational demands.
Selecting the right type of RFID tag
Selecting the appropriate RFID type depends on factors like asset size, movement patterns, environment, and budget. A thoughtful RFID strategy often incorporates multiple types to achieve end-to-end visibility.
Passive RFID Tag: These tags have no internal power source and rely on energy from the RFID reader to transmit data. They are cost-effective and smaller than active tags, making them ideal for tagging a large volume of items and for short-range tracking like bins or items on assembly lines.
Active RFID Tag: Equipped with their battery, these tags can broadcast signals over much longer distances. Active RFID is suited for tracking large assets like containers, trailers, or vehicles across yards or distribution centers.
Semi-passive (battery-assisted passive tags) RFID Tag: A hybrid model combining passive and active tags, these offer improved read range and reliability without the higher cost of fully active tags. They are useful in scenarios needing moderate distance tracking with energy efficiency.
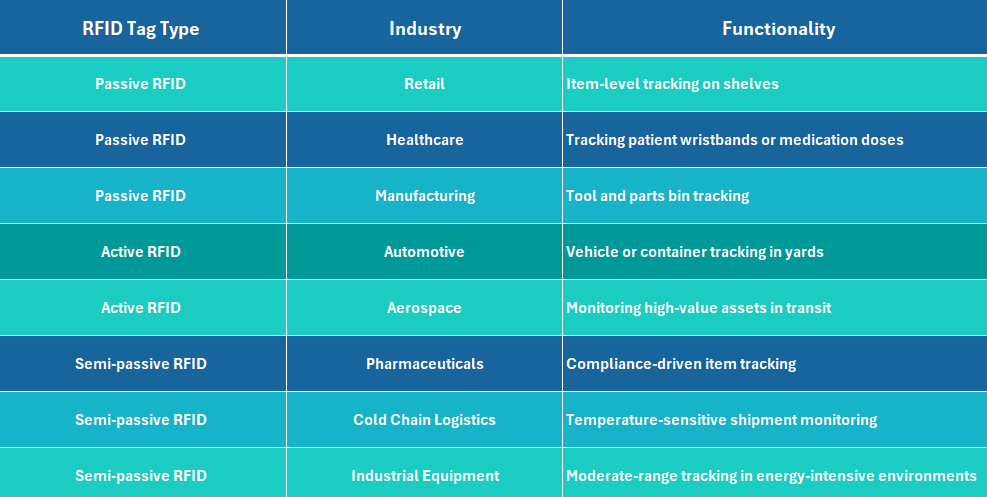
The following comparison table highlights real-world applications of key RFID tag types across industries. By mapping passive, active, and semi-passive tags to sector-specific use cases, this overview helps contextualize their practical roles from item-level tracking in retail to container monitoring in automotive supporting informed technology selection based on operational context.
RFID Tag Type Across Industries
While the earlier classification centered on power source and functionality such as active, passive, or semi sensor-integrated tags it’s equally important to understand RFID tags by their physical form factors and industry-specific naming conventions.
| RFID Industry Tags | Physical Form | Primary Functionality & Use | Typical Environment / Key Advantage |
| Smart Labels / RFID Labels |  | Item-level tagging, retail, and packaging | General inventory, discreet tagging, high volume |
| Paper Tags |  | Wireless data exchange, visual identification, support automated scanning | Pricing, basic labelling, for supply chain, retail, pharma and IOT |
| NFC Tags |  | Consumer engagement, authentication, and short-range data | Retail point-of-sale, product packaging, and smart posters |
| Sensor-Equipped Tags |  | Condition monitoring (temp, humidity, shock) | Cold chain, pharmaceutical, fragile goods logistics |
| High-Temperature Tags |  | Tracking in extreme heat environments | Manufacturing (e.g., automotive paint shops, ovens) |
| On-Metal / Metal Tags |  | Reliable tracking on metal surfaces | IT assets, industrial equipment, and metal containers |
| On-Liquid / Liquid-Friendly Tags |  | Tracking goods containing liquids | Chemical storage, beverage industry, pharmaceuticals |
| Encapsulated / Ruggedized Tags |  | Durability in harsh conditions | Industrial, outdoor, reusable transport items |
| Embeddable Tags |  | Discreet, integrated tracking within products | Manufacturing (source tagging), anti-counterfeiting |
| Button Tags / Disc Tags |  | Durable, compact identification | Industrial assets, tools, and outdoor |
| Laundry/Apparel Tags |  | Withstand washing, drying, and high temps | Healthcare, hospitality, and industrial laundry |
| Cable Tie Tags |  | Secure and identify bundled items | Asset bundling, securing bags/pallets |
| Wristband Tags |  | Access control, event management | Events, healthcare, theme parks |
| Key Tags |  | Access control, personal identification | Office access, residential, and personal items |
| Glass Tube Tags |  | Very small, embeddable identification | Animal ID, medical instruments, and small components |
| Ear Tags |  | Livestock identification | Agriculture, animal husbandry |
| Pocket Tags |  | Personal ID, access control | Employee badges, visitor passes, event entry |
Looking Ahead How RFID and SAP EWM Can Redefine the Warehouse
We recognize that deploying RFID is only one part of a successful digital supply chain transformation. It’s true potential is unlocked when combined with advanced warehouse management systems like SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM):
- This integration enables- automated data capture feeding into warehouse execution
- Real-time inventory updates and dynamic resource allocation
- Enhanced analytics for continuous improvement
RFID-Enabled Inbound and Outbound Process Flows: From GRN (Goods Receipt Note) to PGI (Post Goods Issue)
Traditional inventory counting is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and prone to errors. RFID automates this process by enabling rapid, non-line-of-sight scanning of items, pallets, or bins, significantly reducing cycle count times. Real-time visibility allows teams to detect discrepancies immediately, ensuring accurate stock levels and minimizing stockouts or overstock.
Integrating RFID technology with scalable warehouse management systems like SAP Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) plays a critical role in enabling smooth, efficient, and error-free warehouse operations. SAP EWM serves as the central control system that orchestrates warehouse tasks, while RFID provides real-time item-level visibility and automated data capture. This seamless integration reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and accelerates both inbound and outbound processes, enhancing overall supply chain agility and traceability.
1. Real-Time Visibility in Inbound Process with RFID Integration
Inbound logistics begins when shipments from manufacturing sites arrive at the warehouse. At the inbound gate, RFID antennas capture pallet data automatically using forklift-mounted readers or gate-fixed scanners, triggering receipt events in SAP EWM. As the goods move into the receiving transit area, RFID tags are read again either by handheld devices or through floor-mounted readers, validating pallet identification and enabling traceable handovers to warehouse storage.
This closed-loop RFID capture ensures inbound accuracy, eliminates manual check-in delays, and synchronizes physical movement with system updates in real time. Stellium deployed this system, for a global leader in glass packaging solutions for pharmaceutical, food & beverage, and perfumery businesses, as part of a live project integrating RFID with SAP EWM across inbound operations. Our team optimized RFID placement, SAP EWM configuration, and reader-device orchestration to meet the customer’s real-time visibility and automation goals. This project exemplifies Stellium’s domain expertise and execution capability in RFID-enabled warehouse transformation.
Inbound Process Flow with RFID
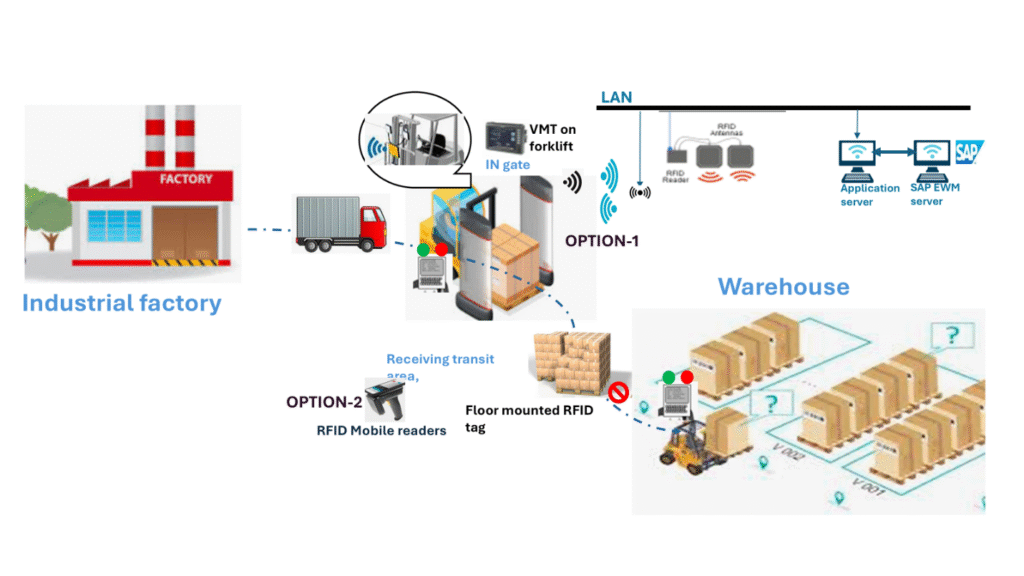
Source: Stellium, presentation materials, 2025.
2. Outbound Fulfillment with RFID-Powered Automation
When powered by RFID and tightly integrated with SAP EWM, the outbound fulfillment process drastically reduces errors and operational delays. The real-time synchronization between RFID systems and SAP EWM ensures precise tracking and control throughout the pick and post goods issue (PGI) cycle:
a. Order Initiation and Pick List Generation
A delivery order placed in SAP EWM automatically generates a pick list, initiating the outbound process and guiding warehouse operations from the start.
b. Material Picking from Storage Bins
Items are picked from assigned storage bins using RFID-enabled systems, where tags are captured either via handheld scanners or fixed readers for seamless identification.
c. Forklift Movement and In-Transit Scanning
As forklifts move picked items, Vehicle Mounted Terminals (VMTs) and RFID readers on board automatically log movement data without manual input.
d. Pre-Dispatch Inspection (PDI) and Tag Validation
At the PDI area, boxes are validated through either handheld RFID readers for manual scanning or floor-mounted readers for automatic detection before dispatch.
e. Outbound Gate Scanning and Confirmation
Outbound loading is confirmed through two methods: automatic updates via fixed RFID readers at the gate or manual confirmation using handheld readers synced with SAP EWM.
f. Post Goods Issue (PGI) and Final Dispatch
Once loading is confirmed, SAP EWM executes the post goods issue, and the shipment exits the warehouse with full traceability and timestamped confirmation.
Outbound Process Flow with RFID
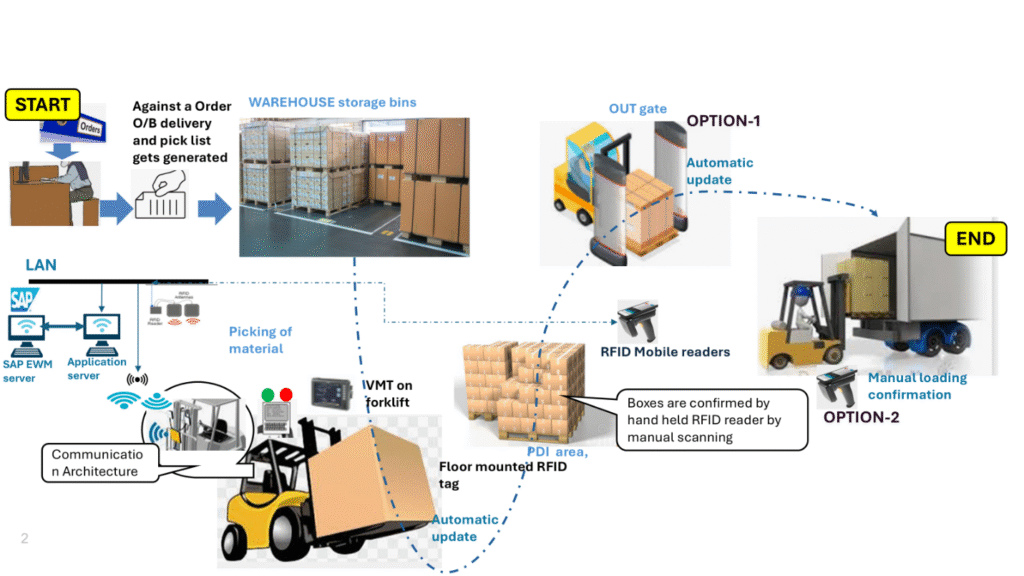
Source: Stellium, presentation materials, 2025.
3. Streamlining Customer Returns and Returns Management
Customer returns present significant challenges in supply chain operations, including verifying product authenticity, tracking lifecycle status, managing aging inventory, and ensuring timely processing. Traditional returns management processes are often manual, error-prone, and lack real-time visibility, leading to delays, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction.
- RFID technology transforms returns management by enabling automated, accurate tracking of returned items throughout their lifecycle. Each product’s RFID tag carries vital data such as manufacturing date, batch number, previous movements, and condition history, allowing supply chain teams to:
- Quickly identify and authenticate returned products without manual inspection, reducing fraud and errors.
- Monitor product aging and shelf life to prioritize refurbishment, resale, or disposal decisions based on real-time condition and lifecycle data.
- Streamline reverse logistics workflows by automating check-in, quality assessment, and routing of returns within warehouses or third-party logistics providers.
- Improve compliance and traceability by maintaining detailed return records, essential for regulated industries and warranty management.
- Enhance customer satisfaction through faster returns processing and transparent status updates.
By integrating RFID-enabled returns management with warehouse execution systems like SAP EWM, companies achieve end-to-end visibility and operational agility, ultimately reducing costs, shortening return cycles, and turning reverse logistics from a cost center into a competitive advantage.
4. Standardizing RFID Label Placement for Consistent Readability
Regardless of whether pallets are moving inbound or outbound, the placement of RFID labels significantly impacts readability and scan accuracy. To ensure seamless tracking:
- RFID labels should be affixed to two opposite sides of each pallet.
- The exact tag location on boxes should be standardized to avoid misreads during scanning.
- One-time-use paper tags with embedded RFID are recommended for cost-effective yet reliable identification.
Standardized RFID Label Placement
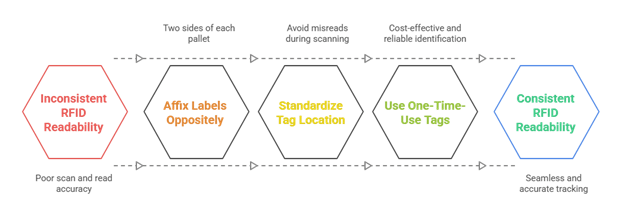
Establishing a tagging strategy upfront enables smooth integration with fixed and handheld RFID readers across processes.
How RFID Drives Supply Chain Success in Retail, CPG and Automotive
In real-world scenarios across diverse industries, RFID technology addresses critical supply chain challenges with proven results. At Stellium, while we’ve delivered solutions in many sectors, here are select examples from automotive, retail, and CPG that showcase measurable improvements in efficiency, visibility, and resilience.
Inventory Accuracy and Omnichannel Fulfillment: A Retail Use Case
A major retail chain struggles with inventory inaccuracies and slow replenishment across multiple store locations. Manual counts and fragmented IT systems cause stockouts and overstock situations, hurting customer satisfaction and sales. RFID enables real-time inventory tracking, automated stock audits, and seamless integration with point-of-sale and ERP systems. This leads to improved shelf availability, faster replenishment, and enhanced omnichannel fulfillment- ultimately increasing customer loyalty and revenue.
This transformation is made possible by RFID’s ability to deliver granular, real-time data across every touchpoint enabling automation, traceability, and actionable insights that traditional systems can’t match.
RFID improves accuracy, security, and efficiency across retail by enabling smarter inventory management, better loss prevention, and streamlined store operations.With real-time stock tracking and quick inventory counts, retailers can maintain optimal stock levels and prevent both overstock and stockouts. Shrinkage control becomes easier as item movement is monitored, reducing theft and inventory discrepancies. On the security front, live monitoring and integrated surveillance systems help detect suspicious activity in real time. Meanwhile, faster checkout speeds and a more efficient supply chain from the warehouse to storefront ensure seamless operations and a better customer experience.
Supply Chain Visibility and Waste Reduction: A CPG Scenario
In the fast-moving consumer packaged goods sector, manufacturers face challenges with expiration management, batch tracking, and recalls. Outdated systems and lack of item-level visibility cause product waste, compliance risks, and slowed response times. RFID adoption provides end-to-end traceability from production to distribution, ensuring precise expiration tracking and swift recall management. This improves regulatory compliance, reduces waste, and enhances overall supply chain resilience.
Stalled Lines and Missing Parts: An Automotive Scenario Where RFID Drives Supply Chain Resilience
A leading automotive OEM faces frequent production line stoppages because critical parts aren’t where they should be. Despite optimized operations, delays arise from misrouted components, incomplete traceability, or outdated inventory data. In a hyper-competitive market where every second counts and customer expectations are high, even small disruptions lead to missed delivery windows, increased costs, and reputational damage.
Cross-Industry RFID Benefits
These challenges are not unique to automotive, retail, or CPG alone. Industries such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and logistics also face similar hurdles with inventory visibility and process inefficiencies. Across sectors, RFID technology enhances supply chain resilience by boosting accuracy, accelerating operations, extending tracking range, and optimizing costs.
Conclusion
At Stellium Inc., we observe a critical disconnect between the physical flow of parts and the digital systems tracking them. The adoption of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology marks a turning point- enabling real-time visibility, anticipating bottlenecks, and driving proactive decisions that bridge the gap between insight and action.
Stay tuned for our upcoming article on RFID Integration with SAP EWM, where we dive into the benefits, improved process visibility, and best practices for seamless implementation.
At Stellium, we don’t just implement these technologies; we architect intelligent, scalable warehouse ecosystems tailored to automotive and high-velocity industries. Our hands-on expertise in RFID calibration, SAP EWM orchestration, and smart device integration positions us to accelerate your digital warehousing goals with confidence.
Learn from Stellium’s Warehouse Automation Services and architect your warehouse with real-time intelligence. Talk to our experts!
