Authored by: Stellium’s Automation Practice and I&ET team and verified by Karthik Krishnan and Hari Babu
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Conveyor systems, STV (Shuttle Transfer Vehicle), EMS (Electrified Monorail System), and SAP Extended Warehouse Management (SAP EWM) are revolutionizing the way warehouses operate.
Rising volumes and labor gaps are pushing companies to adopt layered automation. By integrating ASRS, RFID, conveyors, shuttle systems, AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots), and other automation layers, businesses gain seamless control over material flows while maintaining real-time visibility of every movement.
When combined with AI/ML, these technologies enable predictive decision-making and smarter orchestration under SAP EWM, positioning it as the backbone of future-ready smart warehousing.
By unifying ASRS, RFID, conveyors, shuttles, AMRs, and AI under SAP EWM, operations gain the speed, accuracy, and resilience needed to scale.
This article explains how these layers integrate and how SAP EWM becomes the central orchestration engine for next-generation warehouses.
- Why Warehousing Demands More Than ASRS Alone
- Understanding the Three Pillars of Warehouse
- The Integrated Smart Warehouse Architecture
- How the Automation Layers Interact Within SAP EWM
- Unified Intelligent Automation: ASRS, RFID, Robotics, and AI
- What Makes Stellium’s Automation Expertise Unique
Why Warehousing Demands More Than ASRS Alone
ASRS forms one layer of automation. It relies on supporting systems that move, sequence, and retrieve goods at high speed, such as conveyors and shuttle-based storage.
While ASRS delivers high-density storage and automated pallet handling, real performance emerges only when additional automation layers work together.
Conveyor Systems: Conveyor systems often serve as the backbone of an automated warehouse, providing continuous, high-speed material handling. They efficiently transport, sort, and sequence goods, whether totes, cartons, or pallets, across different zones such as receiving, ASRS, picking stations, and shipping. Conveyors are essential for synchronizing the speed of high-density storage with the pace of order fulfillment.
Shuttle Storage Systems: Shuttle storage systems (also known as ASRS-Shuttle) represent a highly agile and scalable layer of high-speed, high-density storage and retrieval. These systems use robotic shuttles to access individual locations within the rack structure. Unlike traditional ASRS , shuttles offer deep-lane access and can handle high transaction rates for cartons or totes, enabling precise, rapid retrieval and the flexibility to bring specific items directly to workstations as orders are received.
Stellium’s expertise reflects this reality, integrating deep‑lane ASRS, vertical storage systems, AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicle), AMR (Autonomous Mobile Robot),robotics, Conveyors, Shuttle storage systems and intelligent software through SAP EWM and WCS/WES. This multi‑automation approach ensures higher throughput, greater resilience, and real‑time visibility across the warehouse.
Warehouse operations are no longer driven by one system alone, they now depend on a tightly connected ecosystem of automation technologies.
- RFID for automatic, hands-free identification
- ASRS for high-density storage and rapid retrieval and deep lane configurations.
- Vertical storage automation (Carousel, Modula) for compact, high‑density storage.
- AGVs and AMRs for flexible, autonomous goods movement across zones.
- Robotics and shuttles to accelerate order processing and minimize manual handling.
- WCS/WES for synchronized material flow and equipment coordination.
- AI + computer vision for intelligent decision-making and and early anomaly detection.
- SAP EWM as the execution engine, ensuring the right tasks happen at the right time
These combined layers create a warehouse that is faster, smarter, and far more scalable than any ASRS‑only approach.
Understanding the Three Pillars of Warehouse
Automation ASRS: The Physical Automation Foundation
Modern warehouses rely on ASRS as the backbone for automated storage and retrieval. ASRS forms the physical automation layer, using cranes and shuttles to store and retrieve pallets or totes with precision, and robotic lifts maximize vertical space, reduce manual handling, and accelerate fulfillment. SAP EWM and WCS/WES handle planning tasks like sequencing, slotting, and task creation. This keeps physical handling separate from higher-level control and decision-making.
RFID: Real-Time Visibility and Tracking Across Warehouse Movements
RFID creates continuous visibility (explore our RFID in SAP EWM whitepaper) by identifying and tracking products without manual or line-of-sight scanning. Tags, readers, and SAP Auto-ID Infrastructure work together to feed real-time movement data into SAP EWM, eliminating scanning errors and strengthening traceability.
AI & Machine Learning: For Intelligent Orchestration
AI and ML models deliver predictive insights that enhance warehouse decision-making. These models enhance decision-making by identifying patterns, improving slotting strategies, and supporting smarter routing across warehouse operations. Rather than performing full predictive control on their own, these models complement SAP EWM by providing targeted insights that help streamline tasks and reduce potential disruptions.
The Integrated Smart Warehouse Architecture
Below is the architecture of an intelligent, automation-driven warehouse. It shows the five key layers that work together to connect RFID and ASRS systems into SAP EWM and then elevate them with AI/ML intelligence.
Representation of Intelligent Warehouse Automation Architecture
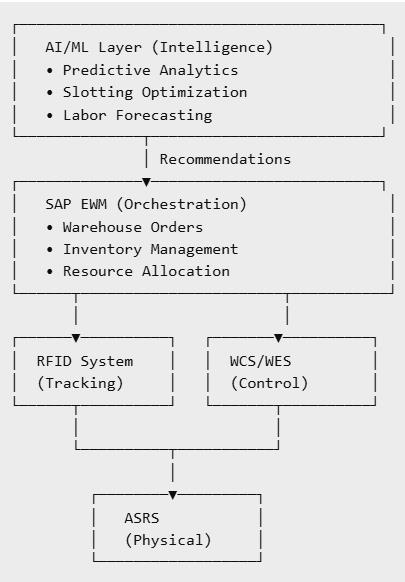
This layered model represents the core principles of warehouse automation when executed through SAP EWM. How the Automation Layers Interact Within SAP EWM
ASRS (Physical Layer): Physical Execution of Storage and Movement
The foundation of warehouse automation begins with Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS). These systems handle pallet storage and retrieval, enable high-density vertical storage, reduce manual labor, and improve speed and throughput. ASRS interacts directly with WCS/WES and SAP EWM through automated messages that confirm picks, putaways, bin movements, and exceptions, ensuring seamless execution of physical warehouse tasks.
RFID System (Tracking Layer) : For Real-time tracking & Automation
RFID technology provides hands-free, real-time identification of pallets, cartons, and totes. By combining RFID tags and readers, warehouses can automatically capture goods movements, pallet entry and exit events, cycle counts, ASRS induction and retrieval scans, and dock-door confirmations. These RFID events feed directly into SAP EWM, eliminating scanning errors and enabling accurate, real-time stock updates across the warehouse.
WCS / WES (Control Layer): Equipment Control & Material Flow Coordination
Warehouse Control Systems (WCS) and Warehouse Execution Systems (WES) act as traffic controllers for machines and ASRS subsystems. They manage conveyors, shuttle cars, pallet cranes, robotics, and routing decisions. While WCS/WES execute the physical actions, SAP EWM determines what must happen and when, ensuring that warehouse operations remain synchronized and efficient.
SAP EWM (Orchestration Layer): Central Orchestration for Warehouse Execution
SAP EWM serves as the brain of the warehouse, orchestrating all activities. It generates warehouse orders, picking tasks, waves, and resource planning while maintaining real-time stock visibility and bin/slot decisions. EWM connects upward to AI/ML systems and downward to WCS/WES and RFID, making it the central execution engine. With its Material Flow System (MFS), SAP EWM can even directly control ASRS without requiring a WCS, further streamlining automation.
AI/ML Layer (Intelligence Layer): Predictive Optimization for Warehouse Operations
At the top, the AI/ML layer delivers continuous intelligence and optimization. It enables demand-driven slotting, predictive workload balancing, exception forecasting, replenishment optimization, labor forecasting, and anomaly detection such as misrouted totes. AI insights flow back into SAP EWM, which adjusts tasks accordingly. WCS and ASRS then execute these tasks, while RFID verifies the outcomes. This closed-loop system creates a self-improving warehouse that continuously enhances efficiency and resilience.
Unified Intelligent Automation: ASRS, RFID, Robotics, and AI Working Together
In a fully modernized warehouse, automation layers no longer operate in isolation, they work as a synchronized ecosystem powered by SAP EWM. ASRS provides high‑density, high‑speed storage and retrieval, while RFID delivers continuous, hands‑free visibility that updates SAP EWM the moment materials move. Robotics expand this automation by transporting pallets, cartons, and totes across zones without delays, and AI strengthens the entire workflow with predictive slotting, labor forecasting, and early anomaly detection. Together, these technologies create a real‑time, self‑optimizing environment where SAP EWM acts as the central decision engine
Why This Architecture Matters for the Future of Warehousing
A fully integrated automation ecosystem built on ASRS, RFID, SAP EWM, and AI deliver measurable improvements across accuracy, speed, and real-time decision-making. The combined effect of physical automation, intelligent tracking, and predictive optimization creates a warehouse that adapts instantly to operational demands.
Key Advantages of Integrated Smart Warehousing with ASRS and RFID within SAP EWM provides:
- Real-Time Inventory Accuracy: RFID and ASRS generate instant confirmations, eliminating manual scans and reducing discrepancies.
- Faster Throughput: ASRS handles retrieval, SAP EWM sequences tasks, and WCS/WES executes them without delays.
- End-to-End Visibility: Every material movement, machine, WCS, EWM, and AI is tracked and optimized continuously.
- Scalable Automation: Start with RFID or ASRS and layer additional automation without changing your core SAP EWM backbone.
- AI-Driven Optimization: Predictive slotting, intelligent replenishment, and workload forecasting move operations from reactive to proactive.
What Makes Stellium’s Automation Expertise Unique
Most consulting firms describe ASRS at a generic level, but Stellium brings specialized, hard‑to‑find expertise across a wider automation landscape. Our capabilities include:
- Single-deep and multi-deep ASRS integration for high-density pallet and tote storage.
- Vertical storage automation such as carousel systems and Modula lift modules for optimized spare-parts and slow-moving inventory handling.
- AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) integration coordinated through WES/WCS and SAP EWM for automated horizontal movement.
- Blended automation ecosystems, combining ASRS, AGVs, conveyors, shuttles, and vertical lifts into one synchronized flow.
- End-to-end orchestration under SAP EWM, allowing every automation layer to operate through a unified execution backbone.
In addition to these strengths, Stellium delivers end‑to‑end SAP EWM automation that unifies digital and physical operations. This includes machine control through SAP EWM MFS, integrated ASRS-AMR-WCS/WES flows, and real‑time visibility via RFID, IoT, and intuitive dashboards. With AI‑driven optimization and full lifecycle delivery, every automation layer operates as one coordinated, future‑ready ecosystem.
Build Your Warehouse with SAP EWM beyond standard ASRS
Modern warehouses outperform competitors when automation systems work together under SAP EWM. By unifying ASRS, RFID, AGVs, vertical storage, and AI-driven intelligence, operations become faster, more accurate, and easier to scale.
Stellium helps enterprises unlock this next level of performance by going beyond standard ASRS deployments and designing multi‑layer automation environments that scale with your operations.
If you’re ready to modernize your warehouse, streamline automation, our experts are here to help. Speak with our SAP EWM specialists 